|
|
|
Note: Much of the text in this reference page comes directly from the Java 1.1 API
documentation.
To view the full API follow these links:
browse
directly
download your
own copy (free)
Warning: the API is big! You don't need most of the classes & methods listed
for CISC 121.
Table of Contents:
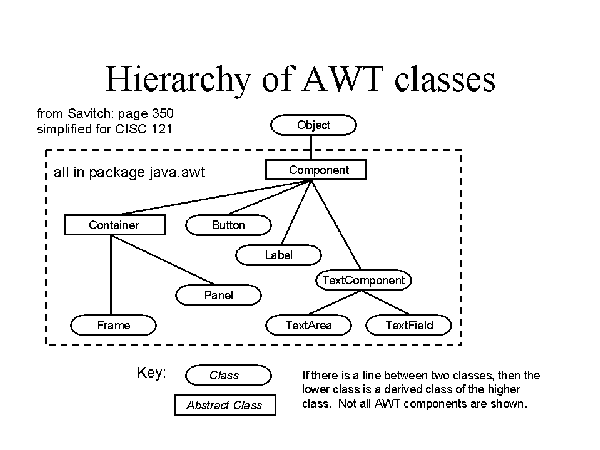
Classes shown in the diagram
Button
Component
Container
Frame
Label
Panel
TextField
Classes not shown in the diagram
ActionEvent
ActionListener
(an interface)
BorderLayout
Color
FlowLayout
Font
Graphics
GridLayout
Button(String label)
Constructs a Button with the specified label.
void addActionListener(ActionListener l)
Registers the specified action listener to receive action
events from this button. Action events occur when a user clicks this button with the
mouse.
see also: Component methods
Component is an abstract class representing any object that can go into a window:
buttons, text fields, and even entire Frames.
void setBackground(Color c)
Sets the background color of this component.
void setEnabled(boolean b)
Enables or disables this component, depending on the value of the
parameter b. An enabled component can respond to user input and generate events.
Components are enabled initially by default.
void setFont(Font f)
Sets the font of this component.
void setForeground(Color c)
Sets the foreground color of this component -- i.e. the color of
letters & graphics.
A Frame is a window, containing a menu bar and the standard Windows buttons (minimize,
maximize, close). The default Layout manager for a Frame is a BorderLayout.
Frame()
Constructs a new instance of Frame that is initially invisible.
Frame(String title)
Constructs a new, initially invisible Frame object with the
specified title
void paint(Graphics g)
Label()
Constructs an empty label.
Label(String text)
Constructs a new label with the specified string of text, left
justified.
Label(String text, int alignment)
Constructs a new label that presents the specified string of text
with the specified alignment. Possible values for alignment are Label.LEFT,
Label.RIGHT, and Label.CENTER.
void setAlignment(int alignment)
Sets the alignment for this label to the specified alignment.
Possible values are Label.LEFT, Label.RIGHT, and Label.CENTER.
void setText(String text)
Sets the text to be displayed in this label.
inherited methods: setBackground, setEnabled, setFont, setForeground from Component
A panel is a sub-area of a Frame. It can have components added to it just like a
Frame. It has its own, independent layout manager for placing components inside the
panel.
Panel()
Creates a new panel using the default layout manager (a
FlowLayout)
Panel(LayoutManager)
Creates a new panel with the specified layout manager.
TextField(String text)
Constructs a new text field initialized with the specified text.
TextField(int columns)
Constructs a new empty TextField with the specified number of
columns.
Sets the text for this label to the specified text.
String getText()
Gets the text that is currently shown in this text field.
void setEditable(boolean b)
Sets the flag that determines whether or not this text field is
editable -- i.e. whether the user is allowed to type into the field.
void setText(String t)
Sets the text that is currently shown in this text field to be
the specified text.
inherited methods: setBackground, setEnabled, setFont, setForeground from Component
An ActionEvent describes a button-click event.
String getActionCommand()
Returns the command name associated with this action (that is,
the label from the button that was clicked).
To implement ActionListener, a class must provide the following method:
void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e)
This is the method that gets called with the user clicks a
button. The argument e describes the button-click event.
A BorderLayout is a layout manager that puts components in one of 5 positions in its
container: North, South, East, West or Center.
BorderLayout()
Constructs a new border layout with no gaps between components.
BorderLayout(int hgap, int vgap)
Constructs a border layout with the specified gaps between
components. The horizontal gap is specified by hgap and the vertical gap is specified by
vgap.
void setHgap(int hgap)
Sets the horizontal gap between components.
void setVgap(int vgap)
Sets the vertical gap between components.
A Color object represents a color that can be displayed on the screen. You can
create colors using RGB values, but for our purposes, just pick one of the constants
provided by the class:
black, blue, cyan, darkGray, gray, green, lightGray, magenta,
orange, pink, red, white, yellow
A FlowLayout is a layout manager that places its components in a row from left to right
until it runs out of room in the window, then starts a new row. A big difference
between FlowLayout and GridLayout is that a FlowLayout leaves its components at their
normal size while a GridLayout stretches them to fill the window.
FlowLayout()
Constructs a new Flow Layout with a centered alignment and a
default 5-unit horizontal and vertical gap.
FlowLayout(int align)
Constructs a new Flow Layout with the specified alignment and a
default 5-unit horizontal and vertical gap. The value of the alignment argument must be
one of
FlowLayout.LEFT, FlowLayout.RIGHT, or FlowLayout.CENTER.
FlowLayout(int align, int hgap, int vgap)
Creates a new flow layout manager with the indicated alignment
and the indicated horizontal and vertical gaps. The value of the alignment argument
must be one of FlowLayout.LEFT, FlowLayout.RIGHT, or FlowLayout.CENTER.
void setHgap(int hgap)
Sets the horizontal gap between components.
void setVgap(int vgap)
Sets the vertical gap between components.
void setAlignment(int align)
Sets the alignment for this layout. Possible values are
FlowLayout.LEFT, FlowLayout.RIGHT, and FlowLayout.CENTER.
A Font object represents a font you can use to write on a Frame.
Font(String name, int style, int size)
Creates a new font with the specified name, style and point
size. The name should be one of the standard Java fonts: "Serif",
"Monospaced", or "Sanserif". The style should be Font.PLAIN or
Font.BOLD or Font.ITALIC (or Font.BOLD + Font.ITALIC to get bold italics). The size
is the size of the font in points.
A Graphics object contains information the system needs to draw on a Frame.
(Other kinds of components can have Graphics objects, but that's beyond what we do in
121.)
void drawString(String str, int x, int y)
Draws a string, given by str. The arguments x and y give the
starting position for the string in pixels, relative to the Frame, not the entire screen.
void setColor(Color c)
Sets this graphics context's current color to the specified
color. All subsequent graphics operations using this graphics context use this specified
color.
void setFont(Font font)
Sets this graphics context's font to the specified font. All
subsequent text operations using this graphics context use this font.
There are many other Graphics methods to draw lines, rectangles, circles, images from
files, etc. See the API for details.
A GridLayout is a layout manager that puts components into a rectangular grid.
GridLayout(int rows, int cols)
Creates a grid layout with the specified number of rows and
columns. All components in the layout are given equal size.
GridLayout(int rows, int cols, int hgap, int vgap)
Creates a grid layout with the specified number of rows and
columns. All components in the layout are given equal size. In addition, the horizontal
and vertical gaps are set to the specified values. Horizontal gaps are placed at the left
and right edges, and between each of the columns. Vertical gaps are placed at the
top and bottom edges, and between each of the rows.
void setHgap(int hgap)
Sets the horizontal gap between components.
void setVgap(int vgap)
Sets the vertical gap between components.